States
Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, WisconsinThe Whitney Genetics Lab and Northeast Fishery Center are partnering to utilize large-scale metabarcoding as another method in the Great Lakes Early Detection and Monitoring program. This initiative is designed to improve the efficiency of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service to detect aquatic invasive species invasive species
An invasive species is any plant or animal that has spread or been introduced into a new area where they are, or could, cause harm to the environment, economy, or human, animal, or plant health. Their unwelcome presence can destroy ecosystems and cost millions of dollars.
Learn more about invasive species early in a potential invasion.
What is Metabarcoding?
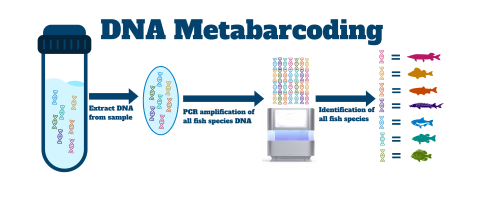
Metabarcoding eDNA is a method that allows biologists to simultaneously identify many taxa from a single sample. For the Early Detection and Monitoring Program, metabarcoding will allow geneticists to amplify a portion of the mitochondrial DNA to potentially identify the species of fish that had DNA collected in an environmental sample.
Benefits of metabarcoding
- Allows biologists to identify many species with one sample, which is more efficient when looking for multiple species.
- With the understanding of which fish species might be present from metabarcoding results, field personnel can equip themselves with the appropriate traditional gear tailored to the specific types of fish they are targeting. The success of capturing a live fish is often contingent upon utilizing correct equipment, as the choice of gear varies based on factors such as fish size, habitat preferences, and behavioral characteristics. A targeted approach significantly improves the likelihood of successful species capture.
- Environmental sampling for metabarcoding can be less time intensive, more sensitive, and less intrusive than traditional sampling techniques.
What stage of development is the Metabarcoding Early Detection and Monitoring program in right now?
- The Metabarcoding Lab at the Whitney Genetics Lab has just been constructed and is now processing samples.
- Lab techniques have been finalized and Standard Operating Procedures are being written on lab procedures.
- We continue to build and improve reference DNA libraries.
- Field offices and other partners are testing metabarcoding sample collection, standard operating procedures, and reporting protocols.